Refrigerant is a working substance that circulates continuously in the refrigeration system and realizes refrigeration through its own state change.
Refrigerant, also known as refrigerant, is commonly known as snow seed in some areas.
Principle: The refrigerant absorbs the heat of the cooled medium (water or air, etc.) in the evaporator to vaporize, and transfers the heat to the surrounding air or water in the condenser to condense.
Its nature is directly related to the refrigeration effect, economy, safety and operation management of refrigeration equipment, so the understanding of refrigerant property requirements can not be ignored.
1. Low pressure and high temperature refrigerant: condensation pressure PK ≤ 2 ~ 3 kg/cm (absolutely), T0>0℃, such as R11(CFCl3), with t0 = 23.7℃. This kind of refrigerant is suitable for centrifugal refrigeration compressor of air conditioning system. Usually at 30℃, Pk≤3.06kg/㎝.

2. medium-pressure medium-temperature refrigerant: condensation pressure Pk<20kg m (absolutely), 0℃="">T0>-60℃. Such as R717, R12, R22, etc., these refrigerants are generally used in ordinary single-stage compression and two-stage compression piston refrigeration compressors.
3. High pressure and low temperature refrigerant: condensation pressure Pk≥20kg/cm (absolutely), T0≤-70℃. Such as R13(CF3Cl), R14(CF4), carbon dioxide, ethane, ethylene, etc. These refrigerants are suitable for the low-temperature part of cascade refrigeration devices or low-temperature devices below -70℃.
Naming method of refrigerant:
(1) inorganic compound-the abbreviation of inorganic compound is specified as R7 (). Parentheses represent a set of numbers, which are integer parts of the molecular weight of the inorganic substance.
(2) The molecular general formula of halogenated hydrocarbon and alkane-alkane compound is cmh2m+2; The general molecular formula of halogenated hydrocarbons is CmHnFxClyBrz(2m+2=n+x+y+z), and their abbreviations are defined as R(m-1)(n+1)(x)B(z).
(3) Non-azeotropic refrigerant mixture-The abbreviation of non-azeotropic refrigerant mixture is R4 (). Parentheses represent a set of numbers, which are the sequential numbers for naming the refrigerant, starting from 00.
(4) Azeotropic mixed refrigerant-The abbreviation of azeotropic mixed refrigerant is R5 (). Parentheses represent a set of numbers, which are the sequential numbers for naming the refrigerant, starting from 00.
(5) Cycloalkanes, alkenes and their halogenated compounds-Symbols stipulate that cycloalkanes and halogenated compounds of cycloalkanes start with the letter "RC" and alkenes and halogenated compounds of alkenes start with the letter "R1".
(6) Organic refrigerants-then they are randomly numbered in the 600 series.
Azeotropic compounds:
A constant boiling point mixture formed by two (or more) liquids is called an azeotropic mixture. (For most liquids mixed with liquids, their components maintain their respective boiling points. However, for a few solutions, their mixed liquid will have a unified boiling point. Once two or more liquids have a common boiling point after mixing, it is called an azeotropic solution. Usually, the boiling point of an azeotropic solution is lower than that of any component constituting this solution)
Common refrigerants
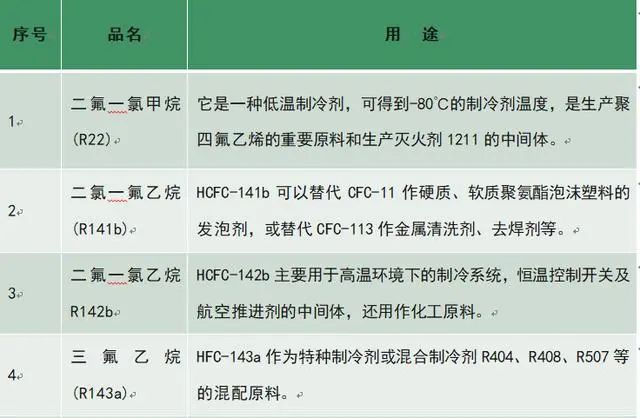
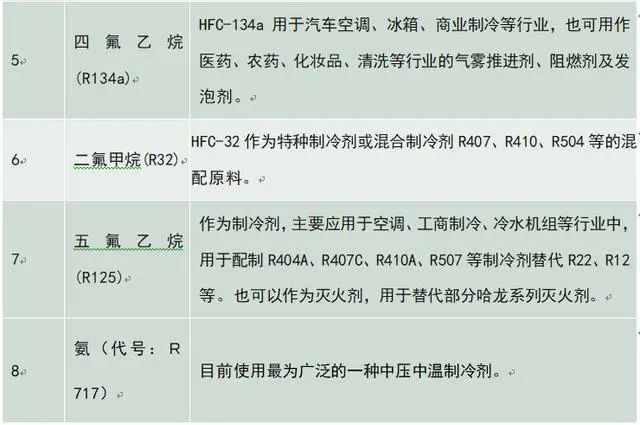



This article is transferred from Refrigeration Network.